
Power Platform Adoption Framework
Adopting, managing, and governing Power Platform at scale
The Power Platform Adoption Framework is the global community standard for adoption, buildout, road mapping, enterprise management and governance of Power Platform at scale within enterprise-grade organizations.
The framework is available on GitHub at https://aka.ms/ppaf, and produced open-source by CloudLight.house for use of the global Microsoft Power Platform community, Microsoft partners and customers alike. Originally created by Andrew Welch, Manuela Pichler, Keith Whatling, Lee Baker, and Lucy Muscat, the first (2019) and second edition (2020) white papers were published with support from Microsoft Partner Applied Information Sciences.
Latest updates and news on the Power Platform Adoption Framework
Organizations must continually mature their Power Platform enterprise management in order to unlock the platform’s value as a first-class cloud application platform and scale it over time. The Enterprise Management Maturity Model is the common standard that can be applied across the platform (and extended across the Microsoft Cloud as well) so that we may assess the maturity of enterprise management and governance, evaluate where an organization has made progress and remains less mature, and identify both organizational risk and opportunities to generate new business value.
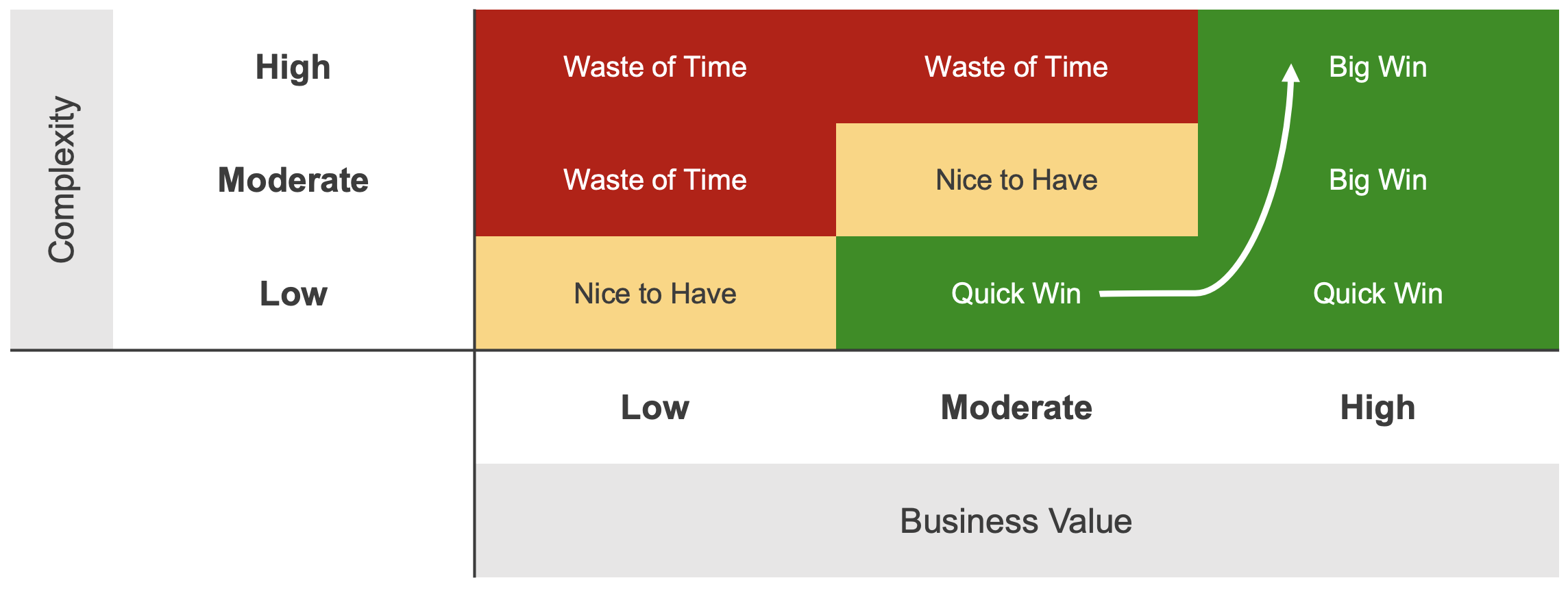
The workload Roadmap is an indispensable part of an organization's ongoing Power Platform adoption. It is a prioritized backlog of workloads that are candidates for migration to or new solution builds on the platform. It allows the organization to project the technology's business value over time, and is the core driver of return on investment in the platform. Here I’ll share the strategy for working directly with business owners, users, and IT to identify, prioritize, and categorize candidate workloads and to create a roadmap for building those workloads on the platform.
Lee Baker, Lucy Bourne, Manuela Pichler, Keith Whatling, and I recently put together seven major themes that we plan to address in the framework over the next six(ish) months. We’d like to share them with the community and ask for your contributions. Each of the themes listed below direct links to their milestone page on GitHub, where you can contribute your ideas, thoughts, approaches, etc. by creating new “issues”. You can also join us in open discussion of all our open issues at this link.
Today we’re releasing the second edition of the Power Platform Adoption Framework. We're introducing some new ideas—and new ways of thinking about existing concepts—as we enter the Power Platform Adoption Framework's second year. As a "framework", we're committed to broadly applicable best practices for adoption at scale, not to being a technical manual.
That’s what low-code cloud transformation and app modernization is really about: Harnessing the “65% Opportunity” with Power Platform as a first-class citizen for business applications amongst Microsoft’s “Three Clouds”. So what's driving this? And — perhaps more importantly — how do we do this at scale? How do we migrate one, two, or ten thousand workloads to Power Platform?
This session introduces the Power Platform Adoption Framework and gives an overview of its start-to-finish approach to help you and your organization get the most value out of any form of Power Platform available to you today. We also share how other enterprise organizations have scaled with large and complex needs using Power Platform and what were the tools, best practices and patterns they explored and used to become successful adopters.
Last week at the PowerApps + Flow User Group in London, I shared the news that ongoing development of the Power Platform Adoption Framework is now happening on Github. Developers everywhere use Github to create software, and now we’re going to use Github to further build the framework that enables people to create beautiful and useful things on Power Platform deployed in large, enterprise-grade organizations.
We need to use Power Platform Adoption Framework as an opportunity to embrace the whole platform, which means thinking about all the component parts — Power BI, Flow, PowerApps (and Common Data Service!) — when we think about enterprise adoption.
I am so excited to be sharing the first edition of the Power Platform Adoption Framework, the start-to-finish approach for adopting Microsoft’s Power Platform at scale. The white paper is available at this link. My hope is that the framework will continue to become a worldwide standard for enterprise-grade adoption of the Power Platform.








Here we’ll lay out a common framework (which we’ll refer to as “C-Frame”) for managing Power Platform solution development. This approach is best suited for solutions that classify as important or critical according to the Environmental Architecture Model found in the Power Platform Adoption Framework. If you take nothing else away from this approach, let it be this: Solution development of important and critical workloads produces far better outcomes and is significantly easier to manage when your team has in its own way accounted for all of these project activities.